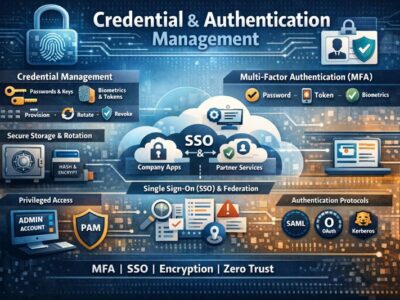
Encryption is a crucial component of network security that provides several benefits in safeguarding sensitive information and communications.
It is one of the most critical action any organization should prioritize in securing their network from threats and vulnerabilities.
Here are 12 benefits of encryption for network security.
Data Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that only authorized parties can access and understand the contents of the data used in an organiztion. This prevents unauthorized individuals or entities from gaining insights into sensitive information.
Data Integrity: Encryption helps maintain the integrity of data by preventing unauthorized modification. If encrypted data is altered during transmission or storage, the decryption process would fail, alerting users to potential tampering.
User Authentication: Encryption can be used in authentication processes to verify the identities of parties involved in communication. This helps prevent impersonation and ensures that data is exchanged only between trusted entities.
Secure Communication: Encryption is essential for securing communications over networks. It prevents eavesdropping and interception of sensitive information by malicious actors, especially in public or untrusted networks.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries and jurisdictions have regulations requiring the protection of sensitive data. Encryption helps organizations comply with these regulations by providing a strong security layer for data protection.
Protection Against Insider Threats: Encryption mitigates the risk of data exposure even if an insider gains unauthorized access. Without the proper decryption key, the data remains unreadable and unusable.
Safe Remote Access: Encryption is essential for securing remote access to corporate networks. Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, for example, rely on encryption to create secure tunnels over the internet.
Security for Stored Data: Encryption safeguards data even when it is stored on devices or servers. If a device is lost or stolen, the encrypted data remains inaccessible without the proper decryption key.
Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Encryption helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties. Even if intercepted, the encrypted data is unreadable without the decryption key.
Defense Against Cyber Attacks: Encryption is a fundamental defense against various cyber threats, including ransomware, data breaches, and information theft. It adds a layer of complexity for attackers, making unauthorized access more challenging.
Secure Cloud Computing: As organisations increasingly adopt cloud services, encryption ensures that data stored and transmitted in the cloud remains secure. This is crucial for maintaining control over sensitive information in shared environments.
Respect for Privacy Rights: Encryption plays a vital role in protecting individuals’ privacy by securing their personal and confidential information. This is especially important in the context of online communication and data storage.
Encryption is a cornerstone of network security, providing a robust defense against a variety of threats and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of sensitive information. Implementing encryption across various layers of network communication is essential for building a secure and resilient infrastructure.