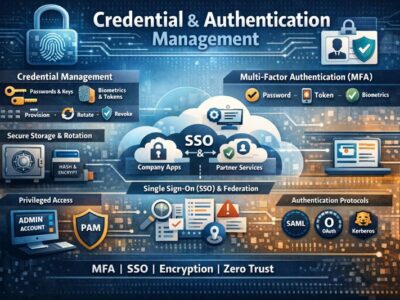
Zero Trust is an integrated defense-in-depth security approach that secures access with adaptive controls and continuous verification across the entire digital landscape. Zero Trust approach ensures that everything on the digital landscape is used to verify access requests and therefore prevent a breach.
In summary, Zero Trust helps to always authenticate and authorize access; use least privileged access and; assume breach at all times. Every access request is verified. The credo of Zero Trust is “never trust, always verify”.
Applying Zero Trust in the Cloud
To create a defense-in-depth cloud strategy using the Zero Trust security approach, areas such as identity, endpoints, data, apps, infrastructure and network access should be highly secured from access.
Many cloud service providers and software manufacturers offer tools to implement Zero Trust in the Cloud. Here, we would be using Amazon Web Service (AWS) solutions to describe the ideas for applying Zero Trust in the Cloud.
Identity
- All users should be migrated to the AWS IAM (AWS Identity and Access Management). AWS IAM will allow modern authentication to new applications and the ability to utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) and AWS IAM policies to govern access.
- Use AWS Cognito for guest users to register within AWS IAM utilizing their current credentials and security policies. This secures guest users from accessing resources that are not assigned to them.
- IAM access policies can be created for groups with their specific IAM roles. Users can be added to these groups when they need temporary administrative access to resources.
- It is important to plan, develop, and use IAM and Service Control Policy to govern over users and the organization and protect sensitive business applications.
- AWS CloudTrail can be used to monitor user and sign-in risks such as brute force identity attacks.
- AWS Inspector and AWS GuardDuty can identify possible threats and vulnerabilities.
- AWS IAM Access Analyzer watches and logs activity for accessing resources.
Data
- Data on applications should be identifies, classified, and protected utilizing sensitivity labels. Amazon Macie can identify sensitive data within AWS S3 storage accounts.
Apps
- Applications that support modern authentication can be registered in AWS IAM to use cloud-native identities for authentication and authorization.
- All devices accessing company resources should be managed with a Mobile Application Management or Mobile Device Management solution.
Infrastructure and Network Access
- Network infrastructure and resources should be designed with Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) segmentation. Resources containing sensitive information should be on their own dedicated VPC.
- Network and Application Security Groups should have rules for how traffic goes through VPC segments and subnets to the private VPC.
In conclusion, identity focuses on user and device access through rules-based access and conditional access policies; endpoints is concerned with managing and securing devices through various security controls; data emphasizes date protection, encryption, and data governance; apps addresses the challenges of controlling access to applications, especially public-facing ones; infrastructure calls for protection of infrastructure in the cloud, providing limited access and permission; and network access involves controlling network access through isolation and segmentation between public and private networks.